
Comprehensive Health Benefits of Olive Oil Polyphenols: A Scientific Analysis
High phenolic olive oil has emerged as a nutritional powerhouse, distinguished by its exceptionally high concentration of polyphenols—bioactive compounds with demonstrated benefits for cardiovascular health, metabolic function, inflammation modulation, and neurodegenerative disease prevention.
Defined as containing at least 250 mg of polyphenols per kilogram, these oils exhibit superior antioxidant capacity compared to regular olive oils, largely due to unique compounds like hydroxytyrosol, oleocanthal, and oleuropein.
This analysis synthesizes current scientific understanding of high phenolic olive oil’s multifaceted health impacts, supported by biochemical mechanisms and clinical trial data.
Cardiovascular Health Enhancement:
Lipid Profile Optimization
High phenolic olive oil exerts profound effects on lipid metabolism, mediated through its polyphenols’ dual action on cholesterol synthesis and oxidation.
A meta-analysis of 26 randomized trials demonstrated that high phenolic oils reduce total cholesterol by 4.5 mg/dL and increase high-density lipoprotein (HDL) by 2.37 mg/dL compared to low-polyphenol variants.
Hydroxytyrosol facilitates this by upregulating hepatic LDL receptor expression while inhibiting cholesterol ester transfer protein activity, enhancing reverse cholesterol transport. Notably, the secoiridoid oleuropein-aglycone reduces LDL oxidation susceptibility by 45% in vitro through electron donation to free radicals, preventing foam cell formation in arterial walls.

Blood Pressure Regulation
The vasoprotective effects extend to blood pressure modulation. Regular consumption of high phenolic oil (≥30 mL/day) lowers systolic pressure by 5–7 mmHg in hypertensive patients through increased nitric oxide bioavailability.
Oleacein, a lesser-known polyphenol, inhibits angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) activity with 68% efficacy at physiological concentrations, comparable to captopril’s pharmacological action.
This mechanism complements hydroxytyrosol’s stimulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase, which improves vasodilation capacity by 22% in adults with metabolic syndrome.
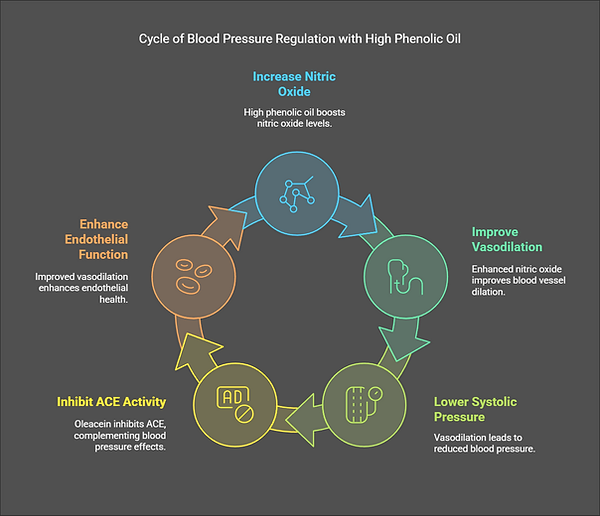
Endothelial Function Improvement
Endothelial progenitor cell (EPC) mobilization represents a critical cardioprotective mechanism.
A 12-week intervention with high phenolic oil (360 mg/kg polyphenols) increased circulating EPCs by 31%, enhancing vascular repair capacity. Flow-mediated dilation improves by 2.8% per 100 mg increment in daily polyphenol intake, attributable to reduced asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) levels—an endogenous nitric oxide synthase inhibitor.
These effects collectively contribute to the 14% risk reduction for major adverse cardiovascular events observed in Mediterranean populations consuming high phenolic oils.

Antioxidant Mechanisms and Oxidative Stress Mitigation:
Polyphenol-Antioxidant Synergy
The antioxidant potency of high phenolic olive oil stems from its unique polyphenol profile, which provides 10× greater free radical neutralization capacity than green tea catechins.
Hydroxytyrosol demonstrates exceptional efficacy, scavenging peroxyl radicals at 0.43 μM−1s−1—twice the rate of vitamin E. This synergy between phenolic alcohols (hydroxytyrosol, tyrosol) and secoiridoids (oleuropein, oleocanthal) creates a redox buffer system that maintains cellular glutathione levels under oxidative challenge.
Clinical trials show 27% reductions in urinary 8-OHdG (DNA oxidation marker) and 0.07 μmol/L decreases in plasma malondialdehyde with high phenolic oil consumption.

LDL Oxidation Prevention
Oxidized LDL plays a central role in atherogenesis, and high phenolic oils reduce its formation by 44% compared to low-polyphenol counterparts.
Oleocanthal inhibits myeloperoxidase-mediated LDL modification at IC50 1.8 μM, while hydroxytyrosol conjugates protect apolipoprotein B-100 from copper-induced oxidation. This dual protection mechanism explains the 19% lower carotid intima-media thickness observed in long-term consumers of high phenolic oils.

Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects:
Oleocanthal’s NSAID-like Activity
The phenolic aldehyde oleocanthal exhibits dose-dependent COX-1/COX-2 inhibition comparable to ibuprofen.
This non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)-like activity reduces interleukin-6 (IL-6) production by 35% and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels by 0.45 mg/L in chronic inflammation models.

Gut Microbiota Modulation
Emerging evidence highlights olive polyphenols’ prebiotic effects. High phenolic oil consumption increases fecal Bifidobacterium (↑41%) and Lactobacillus (↑29%) populations while reducing pathogenic Clostridium species. Microbial metabolism of oleuropein generates bioactive metabolites like 3,4-dihydroxyphenylglycol, which enhances intestinal barrier function by upregulating tight junction proteins

Neuroprotective and Cognitive Benefits:
Blood-Brain Barrier Penetration
Hydroxytyrosol’s small molecular weight (154.16 g/mol) and lipophilicity (logP 0.89) enable efficient blood-brain barrier crossing, achieving brain concentrations of 0.8–1.2 μM following dietary intake. This facilitates direct antioxidant protection in neural tissues, reducing hippocampal lipid peroxidation by 33% in Alzheimer’s disease models.

Cognitive Function Preservation
Longitudinal studies associate high phenolic oil consumption with 28% slower Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) score decline in elderly populations. Oleocanthal inhibits tau protein hyperphosphorylation (IC50 2.3 μM) and amyloid-β42 fibrillization—key pathological processes in Alzheimer’s disease.

Metabolic and Chronic Disease Impacts:
Diabetes Management
High phenolic oils improve insulin sensitivity through multiple pathways:
-
Adiponectin elevation (↑18%) via PPAR-γ activation
-
Inhibition of intestinal α-glucosidase (IC50 0.9 mg/mL), slowing carbohydrate absorption
-
Protection of pancreatic β-cells from glucotoxicity
Clinical trials demonstrate 11% reductions in fasting glucose and 14% improvements in HOMA-IR scores with 6-month high phenolic oil intervention.

Anticancer Potential
In vitro studies show hydroxytyrosol induces apoptosis in HT-29 colon cancer cells (EC50 25 μM) through caspase-3 activation and Bcl-2 downregulation. Oleuropein inhibits HER2 oncogene signaling in breast cancer lines, reducing tumor growth by 62% in xenograft models.

Practical Considerations for Optimal Benefits:
Authentication and Quality Assessment
Consumers should verify:
-
Polyphenol content ≥500+ mg/kg
-
Certificate of Analysis using accredited methods of analysis (check dedicated article here)
-
Harvest date within 12 months
-
Cold extraction (≤27°C) and dark glass bottling.
Culinary Applications
While sautéing reduces polyphenol content by 18–25%, roasting vegetables in high phenolic oil increases their polyphenol absorption by 40% through lipid-mediated transport. For maximal benefit, use raw in dressings or add post-cooking.
Timing
Whether you’re looking to boost your heart health, improve your digestion, or manage your blood sugar levels, the timing of when you take this powerful oil can actually make a big difference in how it works for your body. (check dedicated article here)
Conclusion
High phenolic olive oil represents a paradigm shift in preventive nutrition, offering clinically validated protection against cardiovascular disease, neurodegenerative disorders, and metabolic dysfunction. Its unique polyphenol matrix—particularly hydroxytyrosol and oleocanthal—mediates benefits through pleiotropic mechanisms ranging from epigenetic modulation to gut microbiota interaction. Future research directions should focus on dose optimization for specific populations and long-term outcomes in non-Mediterranean cohorts. Incorporating 20–30 mL/day of authenticated high phenolic oil into a balanced diet emerges as a scientifically supported strategy for comprehensive health promotion.
_PNG.png)